- Introduction
- Variable Identification
- Edit Existing Variable
- Add New Variable
- Search Ontology
- Favorite Terms
- Sub-Samples & Repeated Measures
- Related Tutorial
Introduction
The Breeding Management System’s crop ontology management tool uses a structured vocabulary to allow descriptors to act as variables in database queries and statistical analysis. Core crops come preloaded with a set of variables, or ontology terms, recommended by their community of practice. Preloaded ontologies are fully customizable. The BMS also provides a generic crop database to support any breeding program. Consistent variable definitions are essential for data sharing and collaboration. As you consider ontology customization, we recommend that you coordinate with collaborators and your crop community to similarly define terms to facilitate data sharing and meta analysis. See more about Crop Ontology Curation.
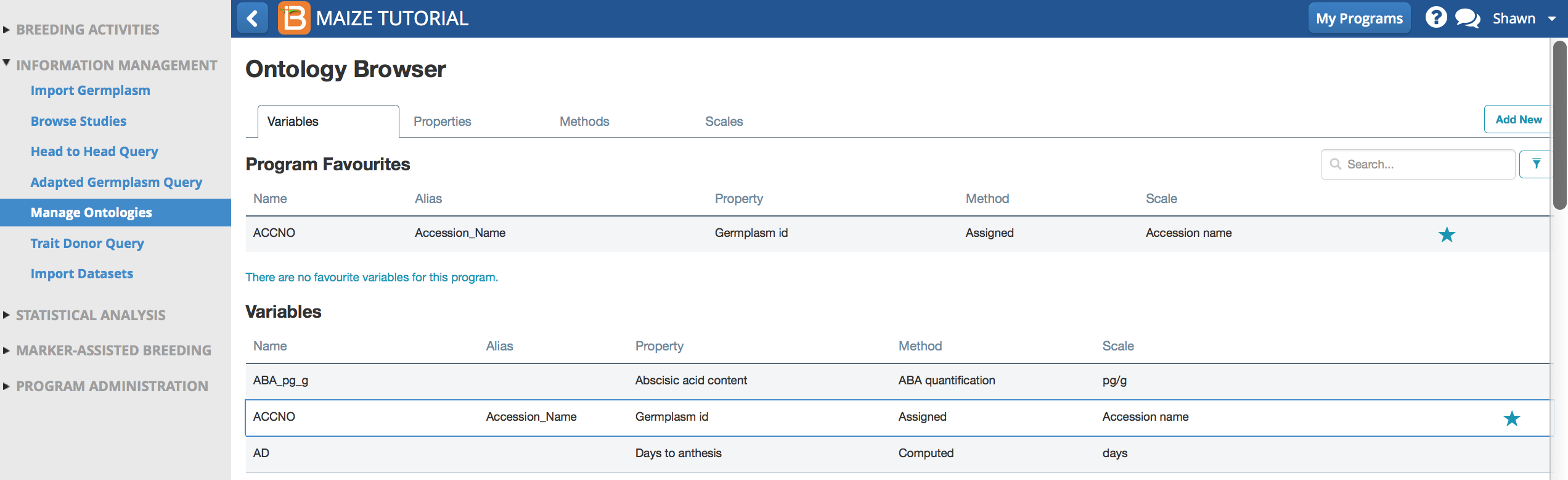
- Select Manage Ontologies from the information management menu to browse, edit, or add ontology terms.
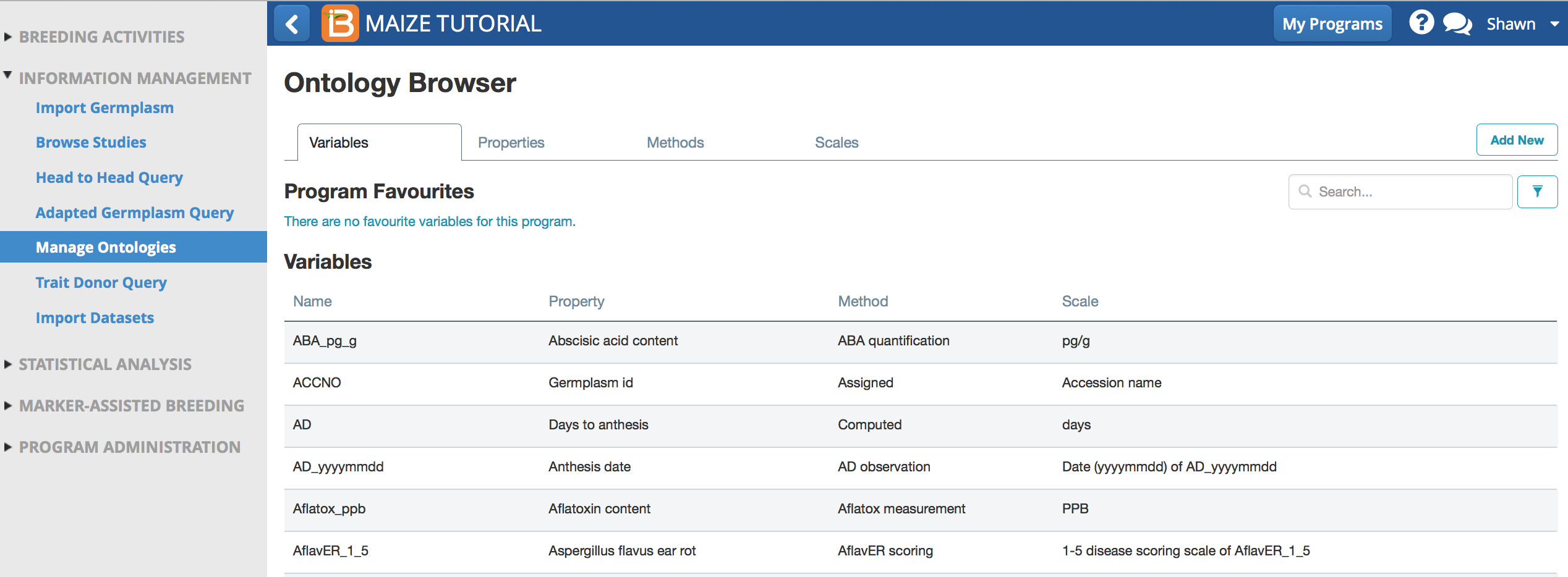
Maize Ontology Browser
Default BMS Trait Dictionaries in Excel File Format
- Wheat Trait Dictionary 4.0 (.xls)
- Soybean Trait Dictionary 4.0 (.xls)
- Lentil Trait Dictionary 4.0 (.xls)
- Rice Trait Dictionary 4.0 (.xlsx)
- Pigeonpea Trait Dictionary 4.0 (.xlsx)
- Cowpea Trait Dictionary 4.0 (.xls)
- Groundnut Trait Dictionary 4.0 (.xls)
- Cassava Trait Dictionary 4.0 (.xls)
Variable Identification
Each variable name is identified by 3 details. Only one ontology term can be associated with a combination of unique details.
- Property: What is measured
- Method: How the variable is measured
- Scale: Categorical scale or unit of measure for the variable
Edit Existing Variable
- Select Edit to change variable details. Once a variable is already in use the database some fields cannot be edited. Editable fields include description and variable type.
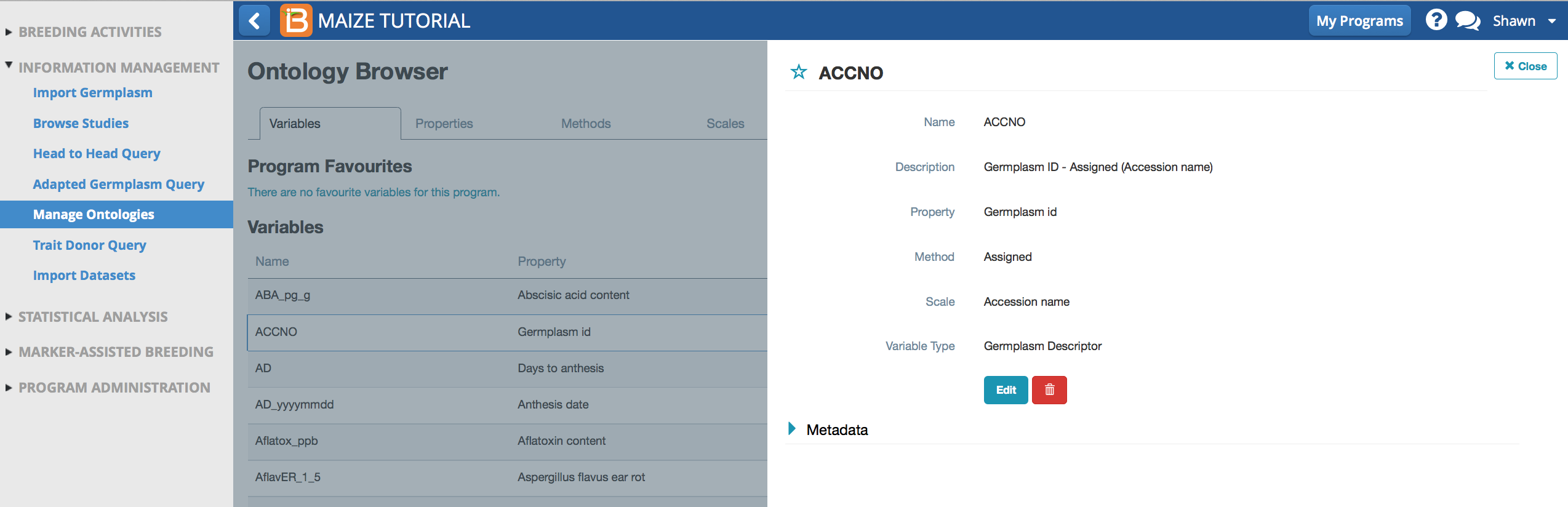
Details about the variable name, ACCNO
The variable can be tagged with additional "variable types" to facilitate search & browse functions.
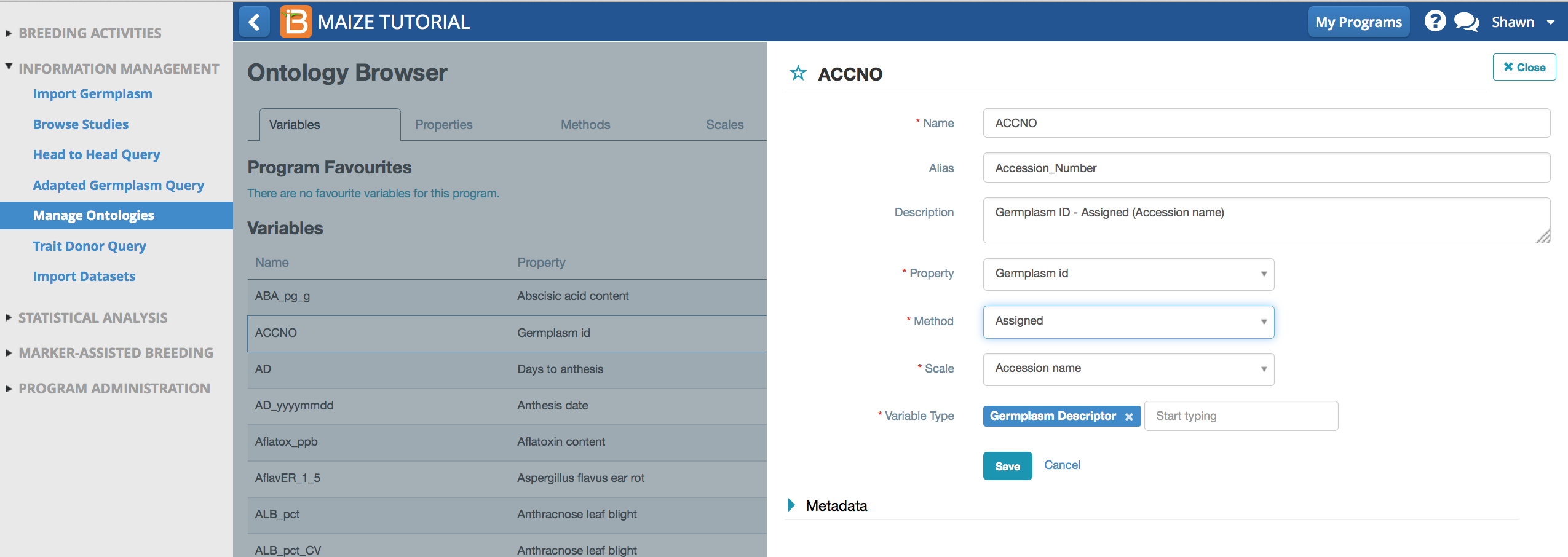 Default Maize Variable, ACCNO, given the alias, Accession_Number. Accession_Number is an assigned germplasm descriptor, an independent variable in statistical analysis.
Default Maize Variable, ACCNO, given the alias, Accession_Number. Accession_Number is an assigned germplasm descriptor, an independent variable in statistical analysis.Variable Name
Variable name is generally an abbreviation or acronym describing the variable. Variable names in the default BMS crop ontology will be recognizable between all members of a crop community. Variable name is the ontology term specified in BMS data collection files and the output of statistical analyses. Variable names cannot contain spaces, numbers, or special characters to ensure compatibility with Breeding View (BV) statistical engine. If variable names exceed 15 characters truncation of variable name will occur in in the graphical output of BV. Changing a variable name does not change the functional identity (property, method, and scale) of the variable.
Variable Alias
Although it is important for crop communities to similarly define traits and share a common vocabulary, the BMS provides the ability to create custom aliases for ontology terms, allowing breeders to communicate variables in familiar language within their breeding programs. Once an alias has been set, the custom alias will replace the variable name in the user interface, data collection files, and the output of statistical analyses. Giving a variable an alias does not change the functional identity (property, method, and scale) of the variable. Variables which are given aliases are automatically added to your program favorites.
Variable Definition
Variable definition is a plain language description of the variable. Editing or expanding a variable's definition does not change the functional identity (property, method, and scale) of the variable.
Add New Variable
- Select Add New. Choose Variable.
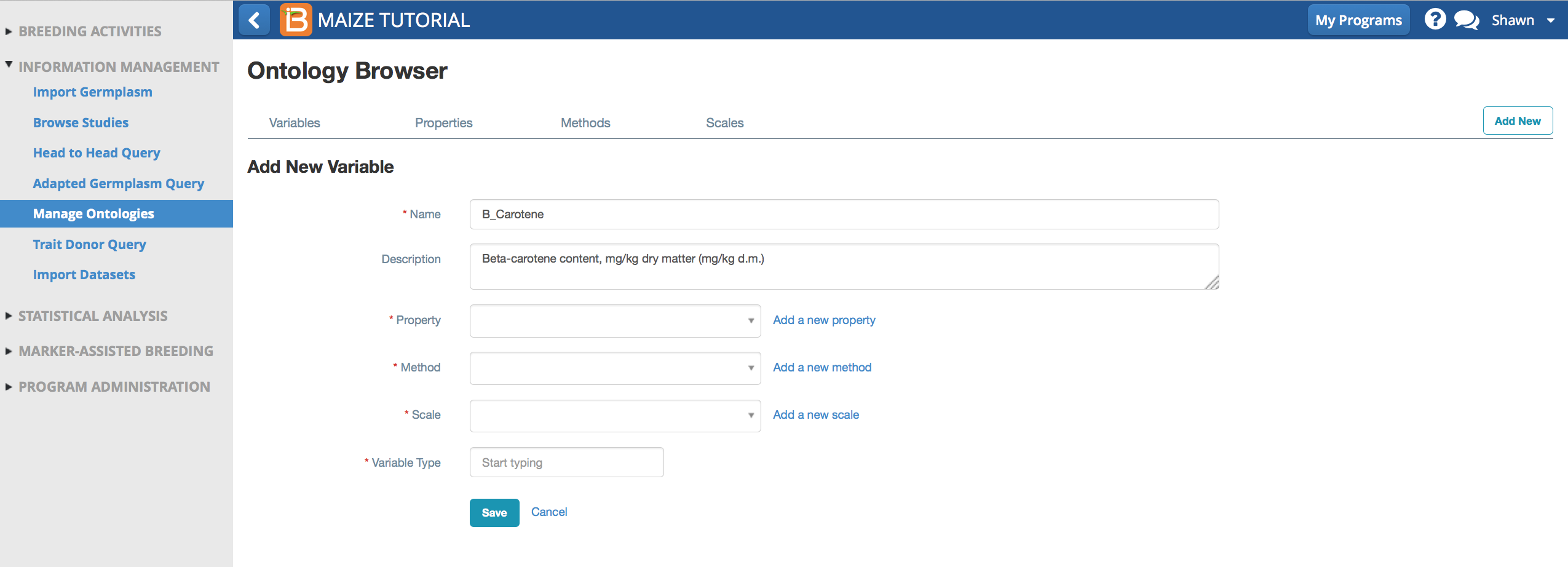
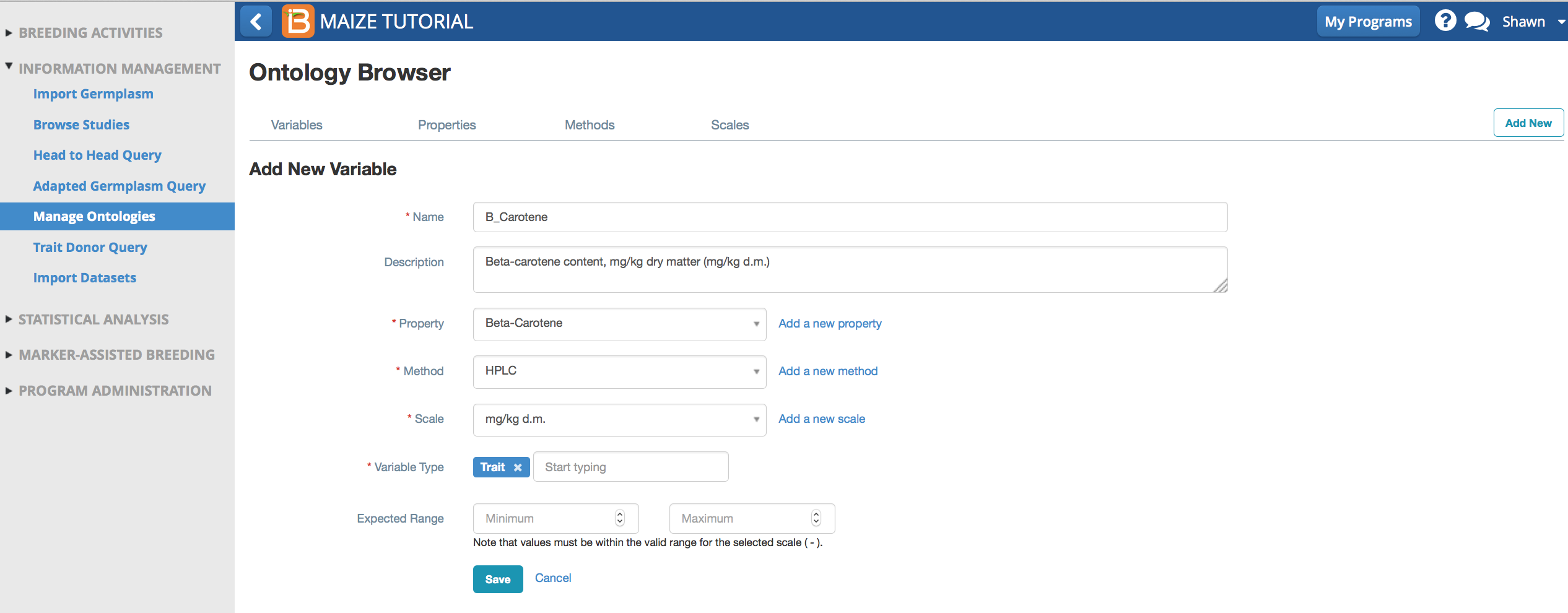
Name & Describe Variable
- Add a new biochemical trait to the the maize ontology.
- Name: B_Carotene.
- Describe: Beta-carotene content, mg/kg dry matter (mg/kg d.m.)
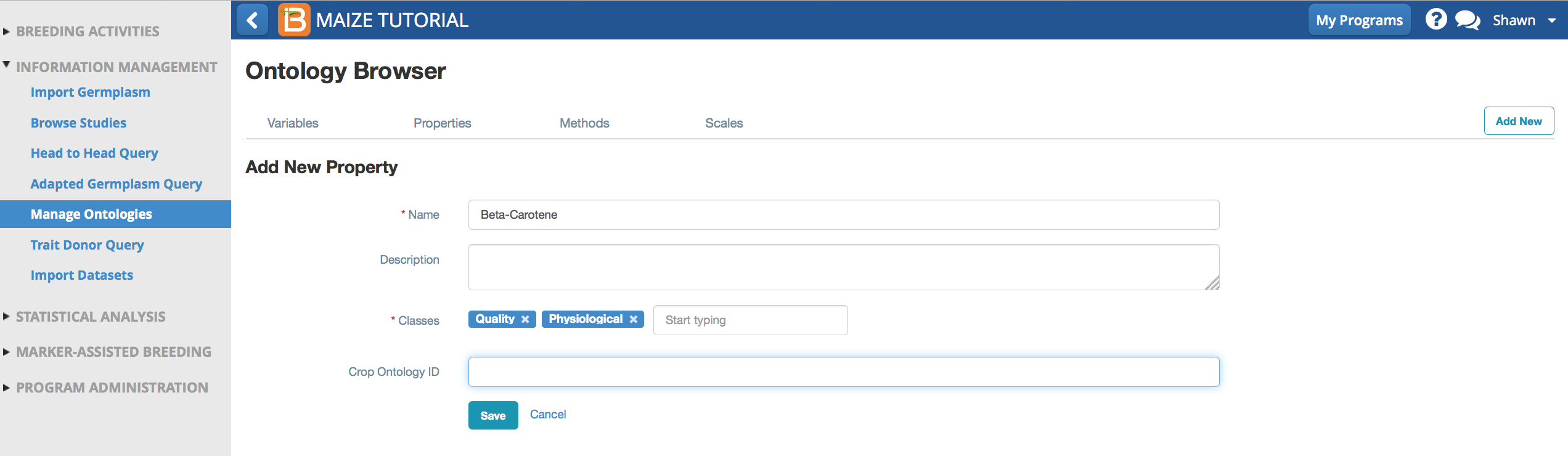
Add New Property
Property describes what is being measured. The default maize ontology has no property describing beta-carotene content, so a new one must be added.
- Select Add a New Property.
- Name the property, Beta-Carotene. Tag the classes, Quality and Physiological. Tagging the property helps the ontology search engine provide selections of relevant traits. Save.
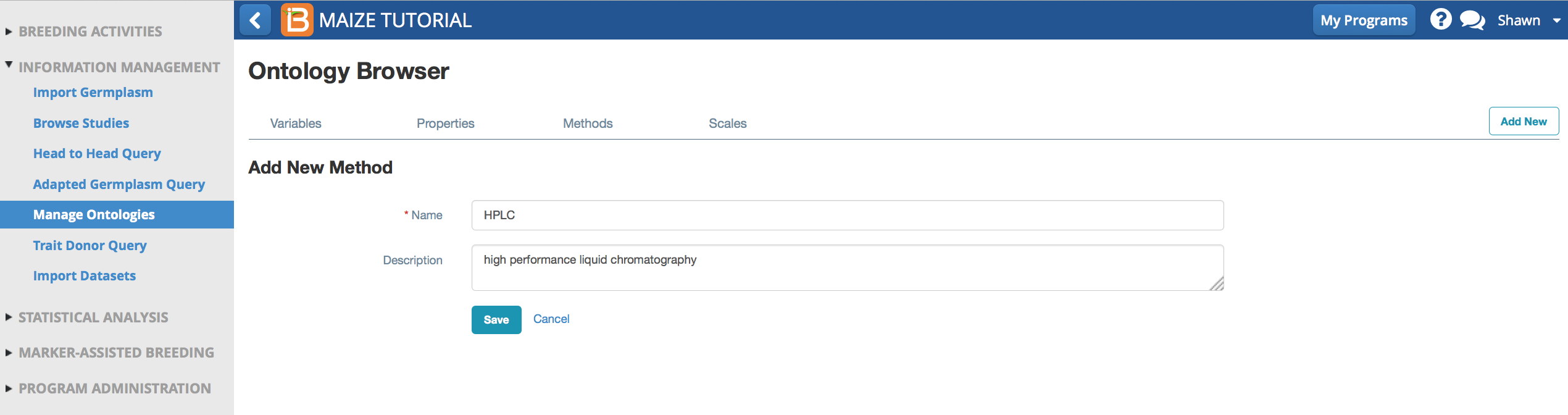
Add New Method
Method describes how the property is measured. Beta-carotene content is measured by high performance liquid chromatography, which is not included in the default maize ontology.
- Select Add a New Method. Name and describe the method, HPLC, high performance liquid chromatography.
Add New Scale
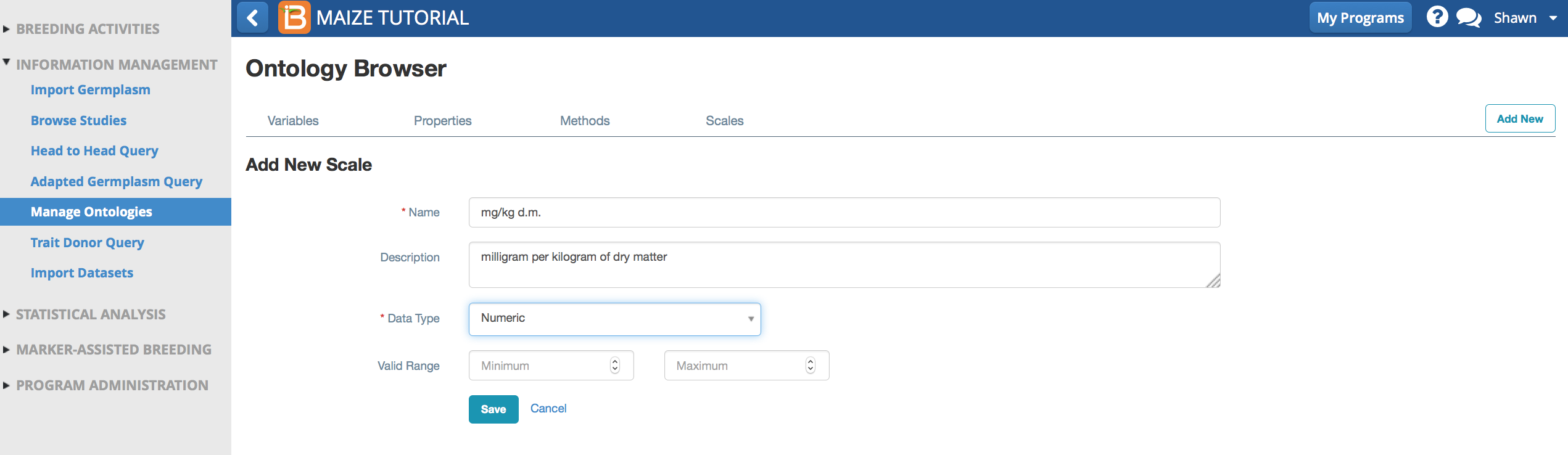
Beta-carotene content is a numeric variable measured in units of milligram per kilogram of dry matter.
- Name: mg/kg d.m.
- Description: milligram per kilogram of dry matter
- Data Type: Numeric
- Valid Range: Numeric variables offer the option of setting a range of valid values for quality control. Data outside of this range is flagged as a possible error during data import.
Variable Type
Variable type differentiates traits, or phenotype, from different independent variables. Variable type determines which variables are presented in different BMS tools.
- Trait
- Analysis
- Environment Detail
- Germplasm Descriptor
- Nursery Condition
- Selection Method
- Study Detail
- Treatment Factor
- Study Detail
- Like most terms in the crop ontology, beta-carotene, is a trait or phenotype. Select Trait from the drop down menu of different variable types. Save.
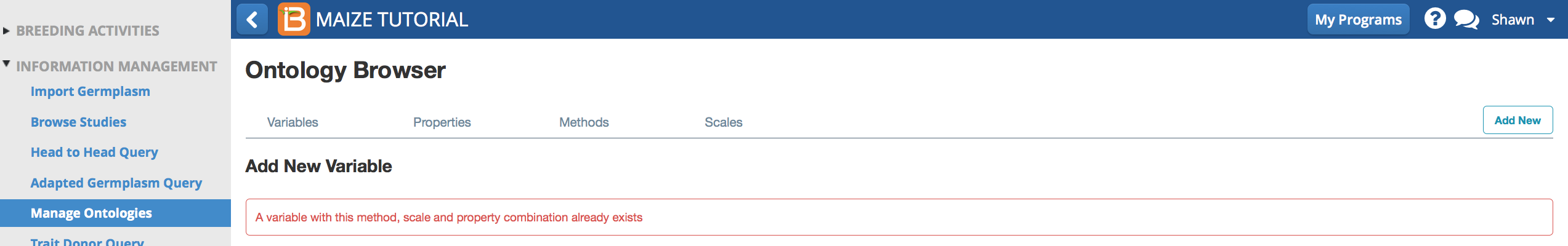
Duplicate Variable Error
The BMS will not allow you to add a new variable with an identical combination of property, method, and scale to other variables.
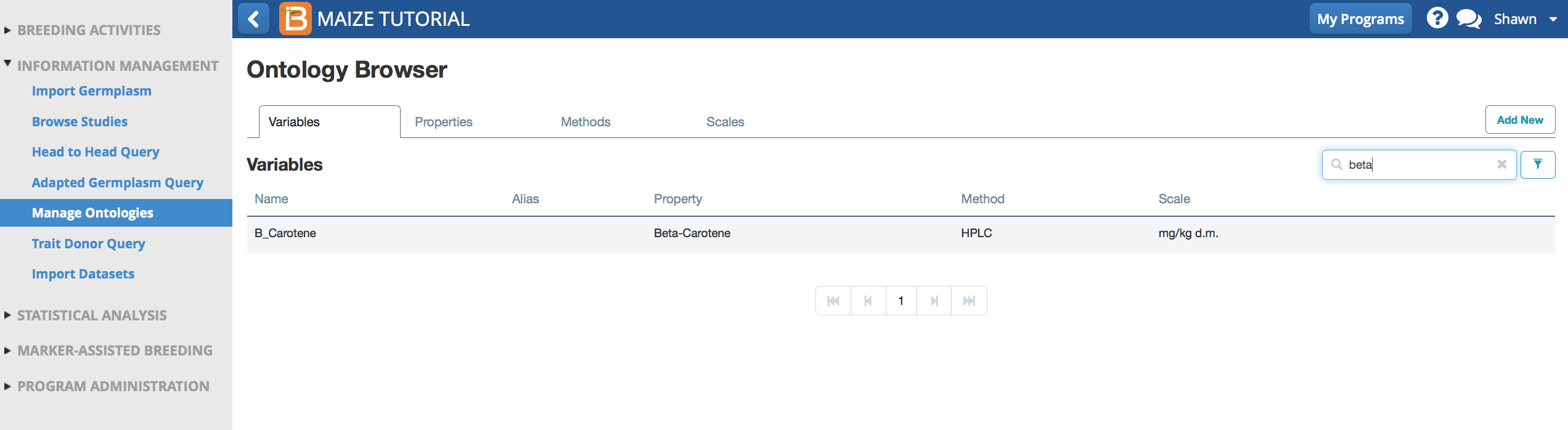
Search Ontology
Searching the maize database for "beta" now reveals the newly added B_Carotene variable.
Favorite Terms
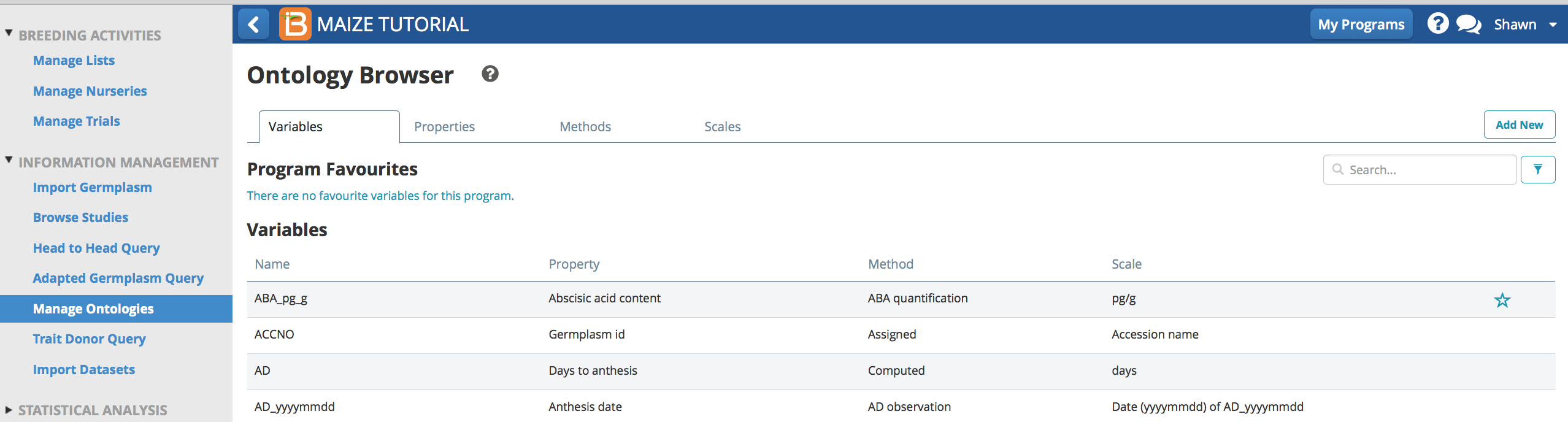
Users can select terms to add to their program's favorites list.
- Scroll the cursor over an ontology term to reveal a blue star. Select the blue star to save the associate term in the program favorites. Alternatively, giving a term an alias (see above) automatically results in that term joining the favorites list.
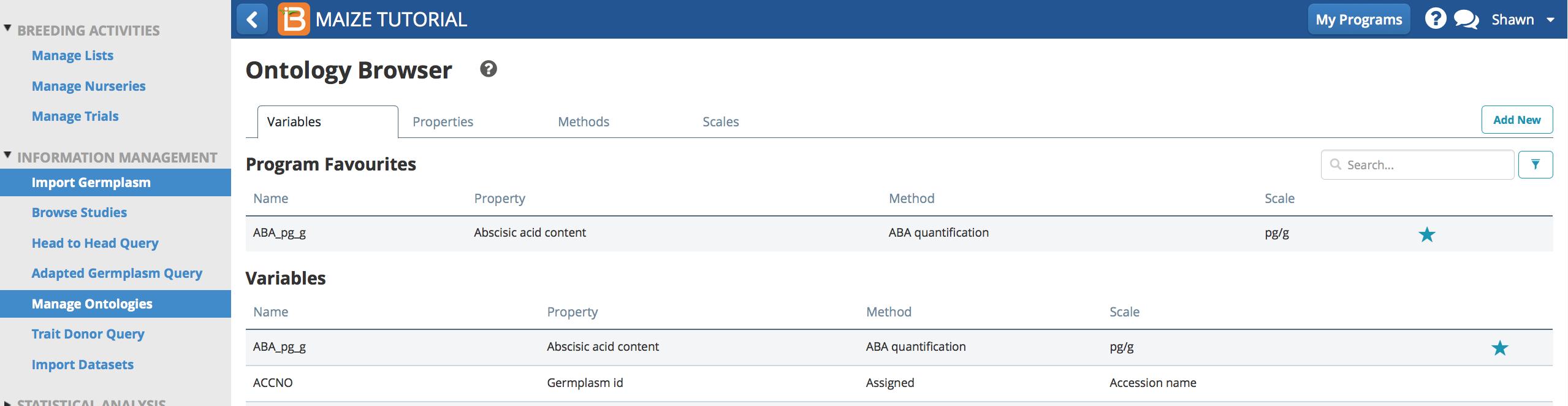
- Several places in the BMS allow users to narrow their search by program favorites, making ontology term selection much easier. Select the star from the favorites list to remove the term.
Sub-Samples & Repeated Measures
BMS version 4.0 does not allow a single ontology term to be associated with sub-samples and repeated measures. (Expect see this flexibility in future versions of the BMS.) Take acid abscisic acid concentration for example. A breeder may want to measure this trait on multiple maize ears per experimental plot or at multiple time points. The current solution is to create multiple ontology terms for each measurement.
- New ontology terms need to be created by adding a sub-sampling or time series code to both the variable name and method. Ideally subsampling and time series nomeclature should be standardized for each crop.
| Sub-Sampling Unit | Code | Examples |
| Sub-sample | s | s1,s2... |
| Quadrat | qdt | qdt1, qdt2... |
| Plant | plt | plt1, plt2... |
| Leaf | lf | lf1, lf2... |
| Stem | st | st1, st2... |
| Tiller | tlr | tlr1, tlr2... |
| Branch | bch | bch1, bch2... |
| Flower | flr | flr1, flr2... |
| Fruit | frt | frt1, frt2... |
| Spike | spk | spk1, spk2... |
| Ear | ear | ear1, ear2... |
| Pod | pod | pod1, pod2... |
| Seed | sd | sd1, sd2... |
| Grain | grn | grn1, grn2... |
| Root | rt | rt1, rt2... |
| Tuber | tbr | tbr1,tbr2... |
| Time Code Type | Time Code | Examples |
| Cereals Zadoks growth/development stages | GS(00-99) or DS(00-99) |
|
| Maize growth/development stages | Vegetative: VE, V1-Vn, VT Reproductive: R1-R6 |
|
| Soybean growth/development stages | VE, VC, V1-Vn, R1-R8 |
|
| Generic Codes |
| |
| Days after emergence | dae | 45dae, 65dae.... |
| Days after sowing | das | 45das, 65das... |
| Days after planting | dap | 45dap, 65dap... |
| Weeks after planting | wap | 1wap, 2wap... |
| Months after planting | map | 1map, 2map |
| Date | yyyymmdd | 20150315 |
| Date+hr+min | yyyymmdd | 201503151135 |
| Time | t | t1, t2... |
- First create a new method with the subsampling code.

- Second create a new trait with the subsampling code.
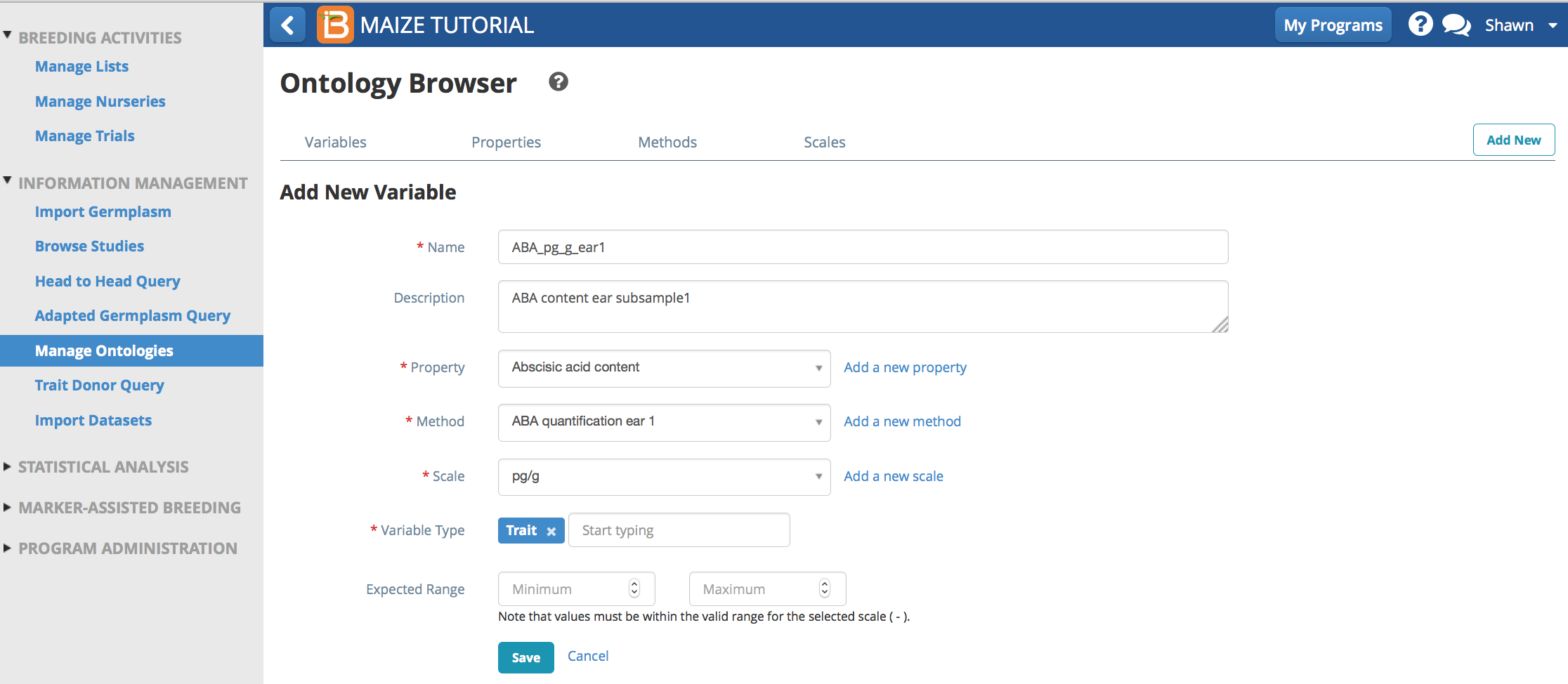
- Repeat. Create a new ontology term for each required sub-sample or time series measurement.