About Advancement
Advancements of selected germplasm generally use maintenance or derivative breeding methods - resulting in offspring less than or equal to the parent(s) in genetic diversity. Advancement can be made by plot or within plot selections. A breeder will chose to advance germplasm for a variety of reasons. Examples include:
- Advance F1 generation to create GIDs for F2 offspring
- Advance plants of interest to create GIDs for the offspring or clones
- Advance inbred lines to create GIDs for bulked seeds
- Advance a bag of seed to create GIDs for individual seeds/seedlings
Advance by Plot
The following example every plot will be advanced, such as for a seed bulk.
- Open a study measurements tab. Select Advance Study from the Actions button dropdown menu.
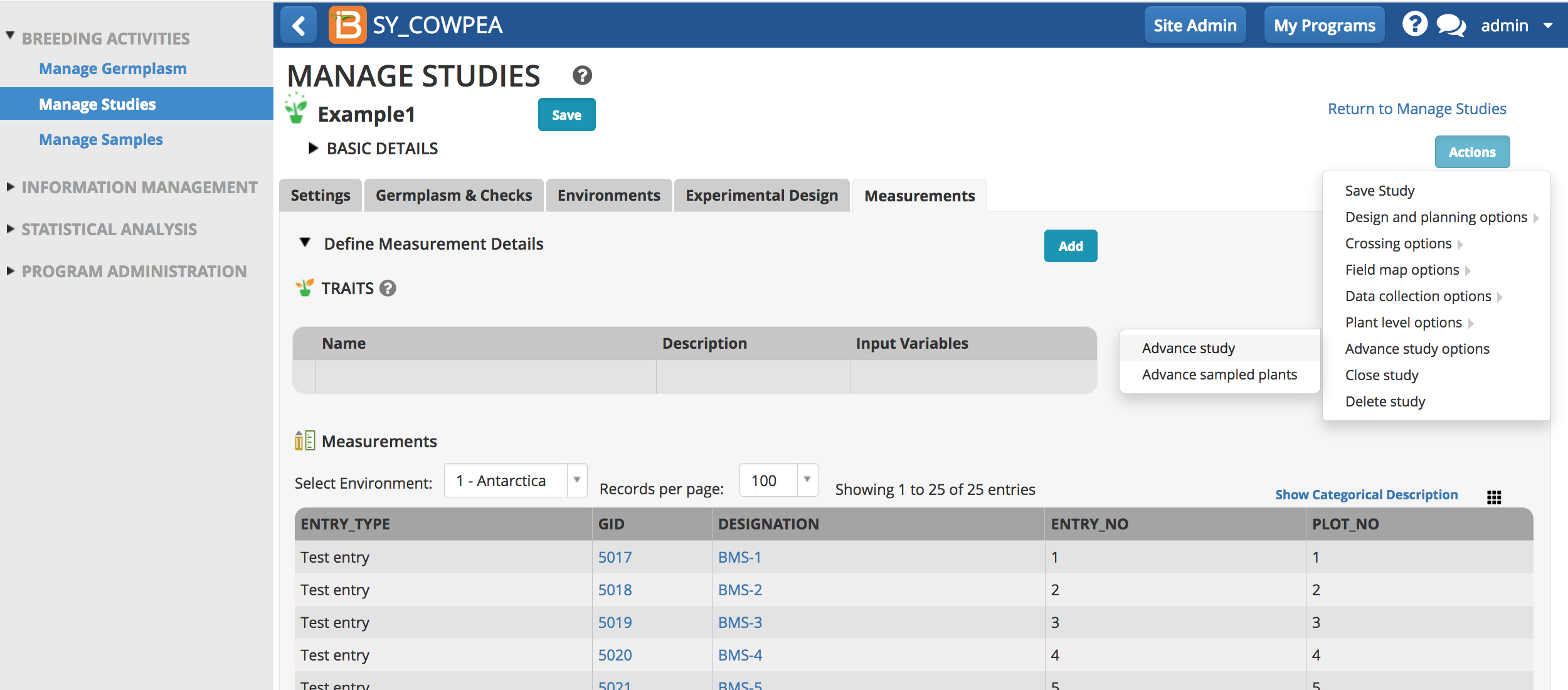
- Select which of the study instances (locations in this case) to advance. Continue.
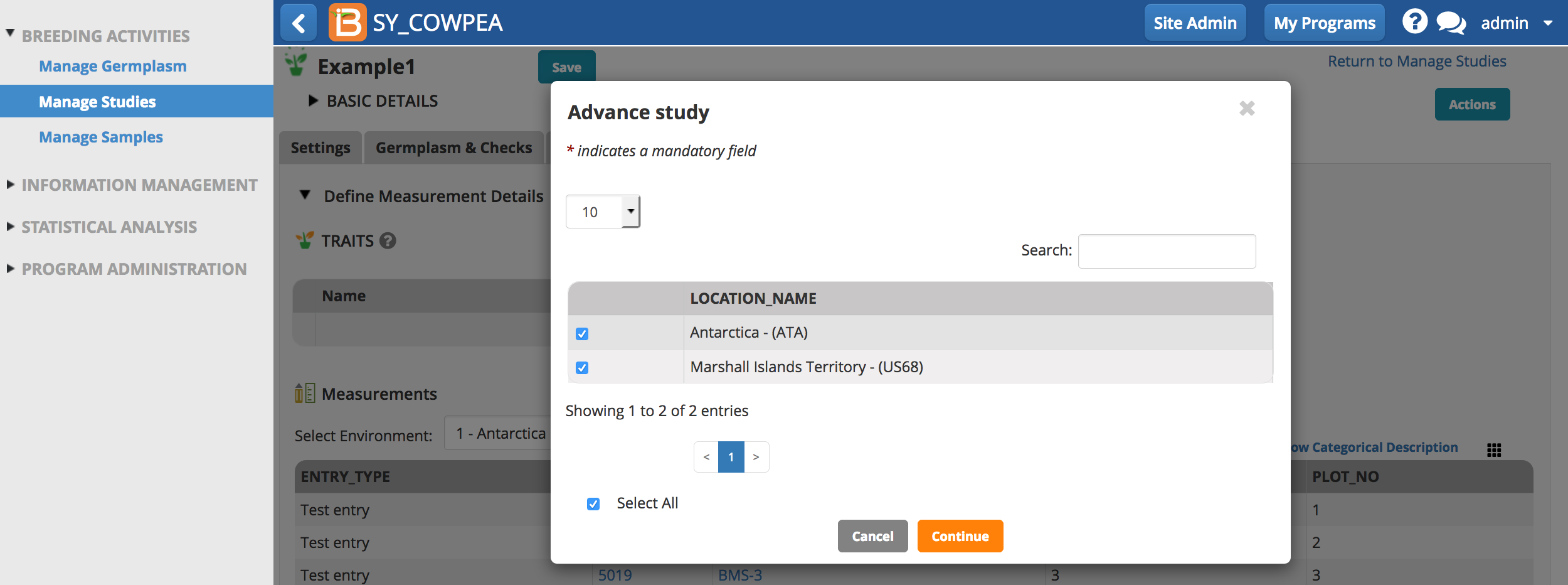
- Choose a breeding method and Finish. Derivative and maintenance breeding methods are filtered by default since these are the most common for advancements. All plots are selected by default.
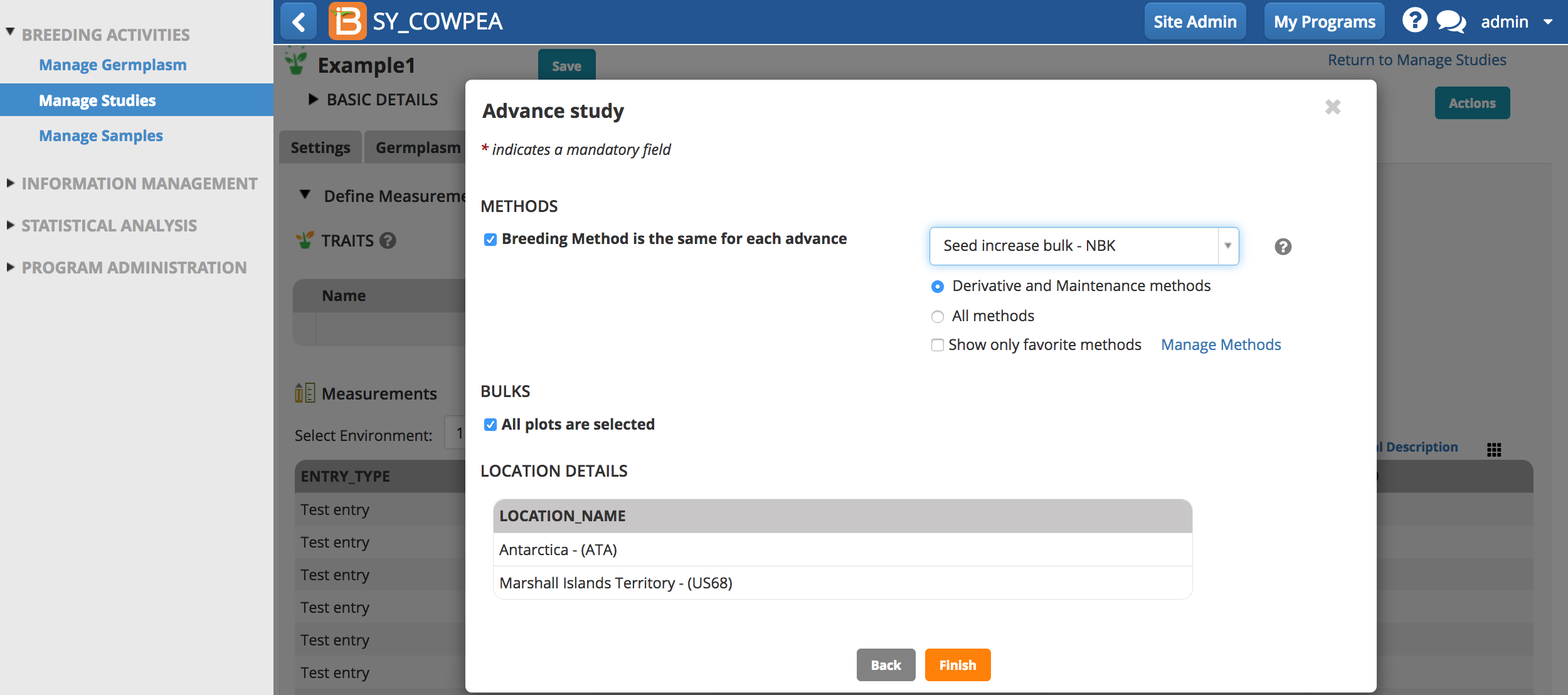
- Review the advanced lines and select Finish.
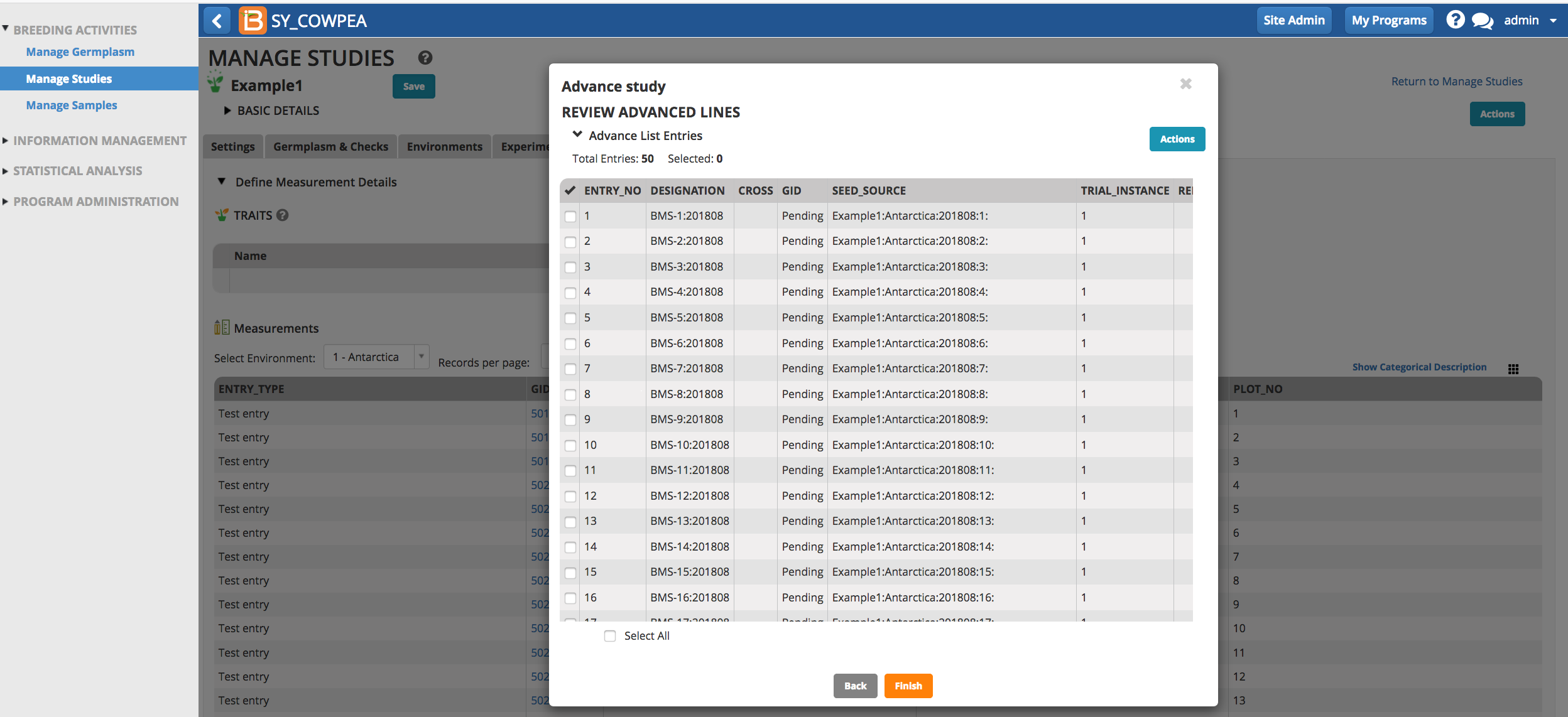
Notice that the pending lines have been automatically named. For example the designation, BMS-1-201808, is a concatenation of the parent line, BMS-1, and the year and month of creation. This is the default naming convention associated with the breeding method, Seed increase bulk. See your system administrator if you would like to change the default naming conventions.
-
Specify the folder where the list will be saved. Name the list and add optional information. Save.
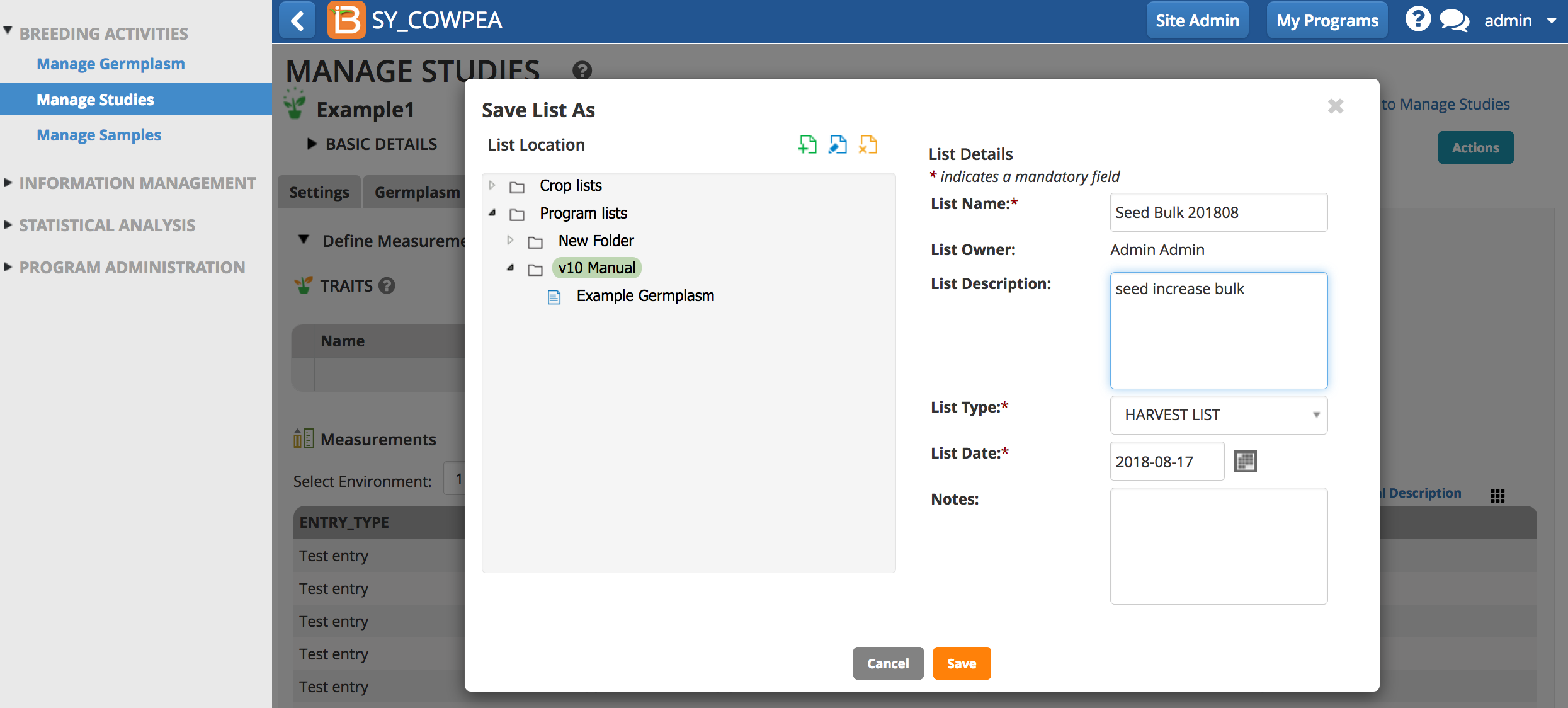
Within Plot Selections
Within plots selections are made based on phenotypic or genotypic criteria. To make within plot selections, the study needs a Selection Variate with selections recorded.
No Plant ID
Selection and advance anonymous plants within a plot.
- From the Actions menu choose Advance Study. In this example, number of plants selected (NPSEL) is a selection variate. A single plant from each plot with disease resistance (zero or one scores for mosaic virus severity) have been selected for advancement.
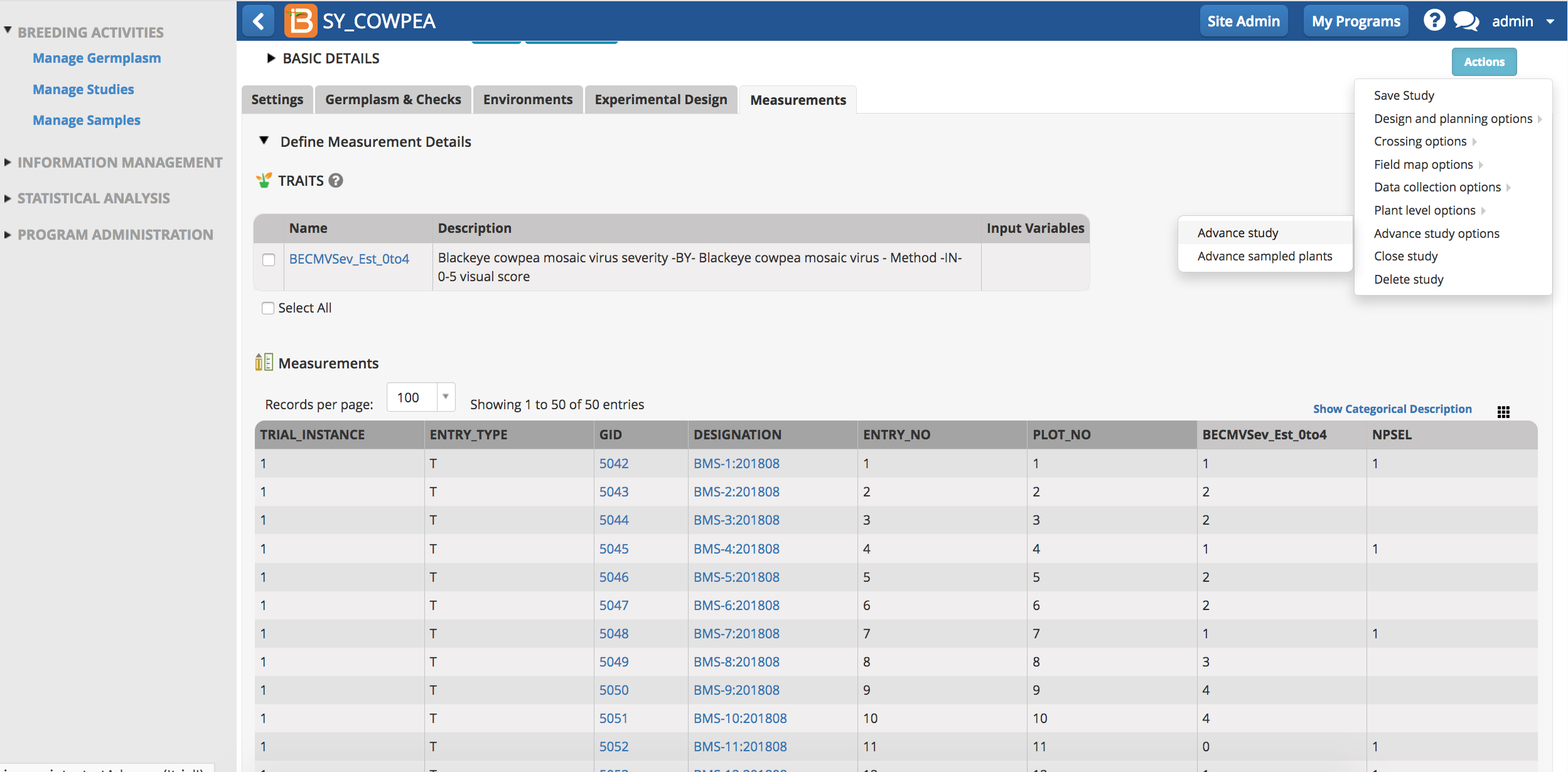
- Select which of the study instances (location in this case) to advance. Continue.
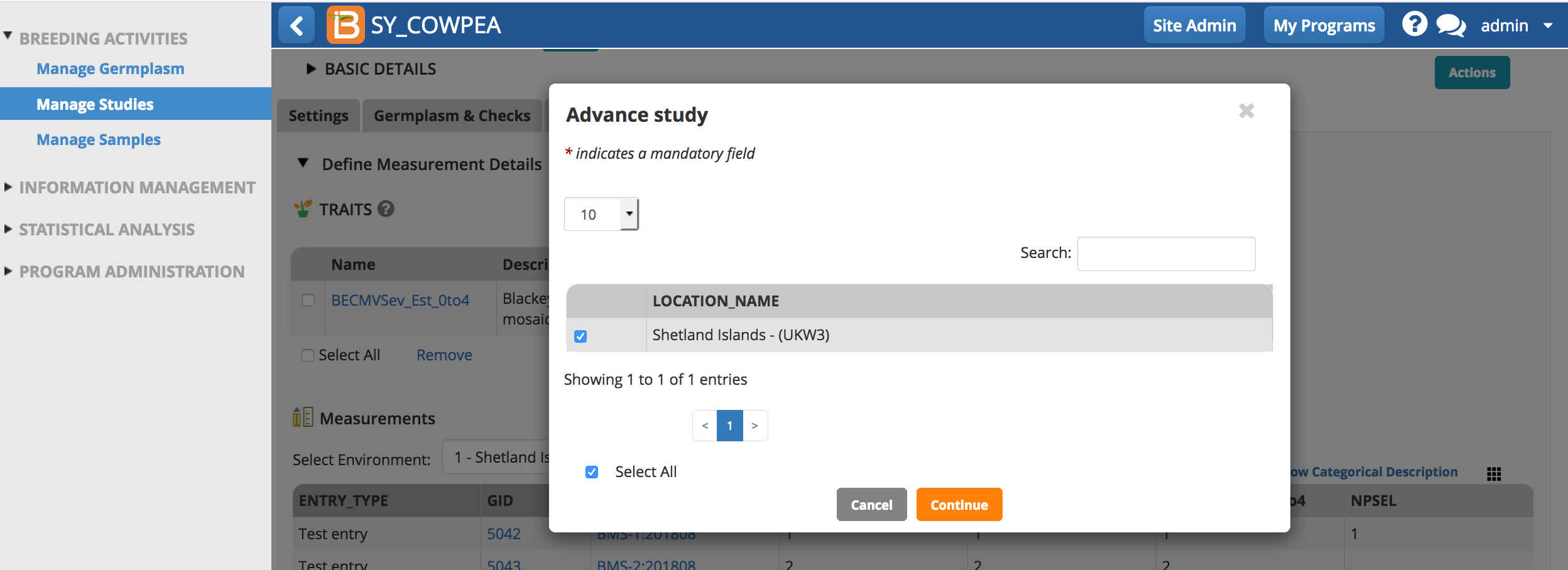
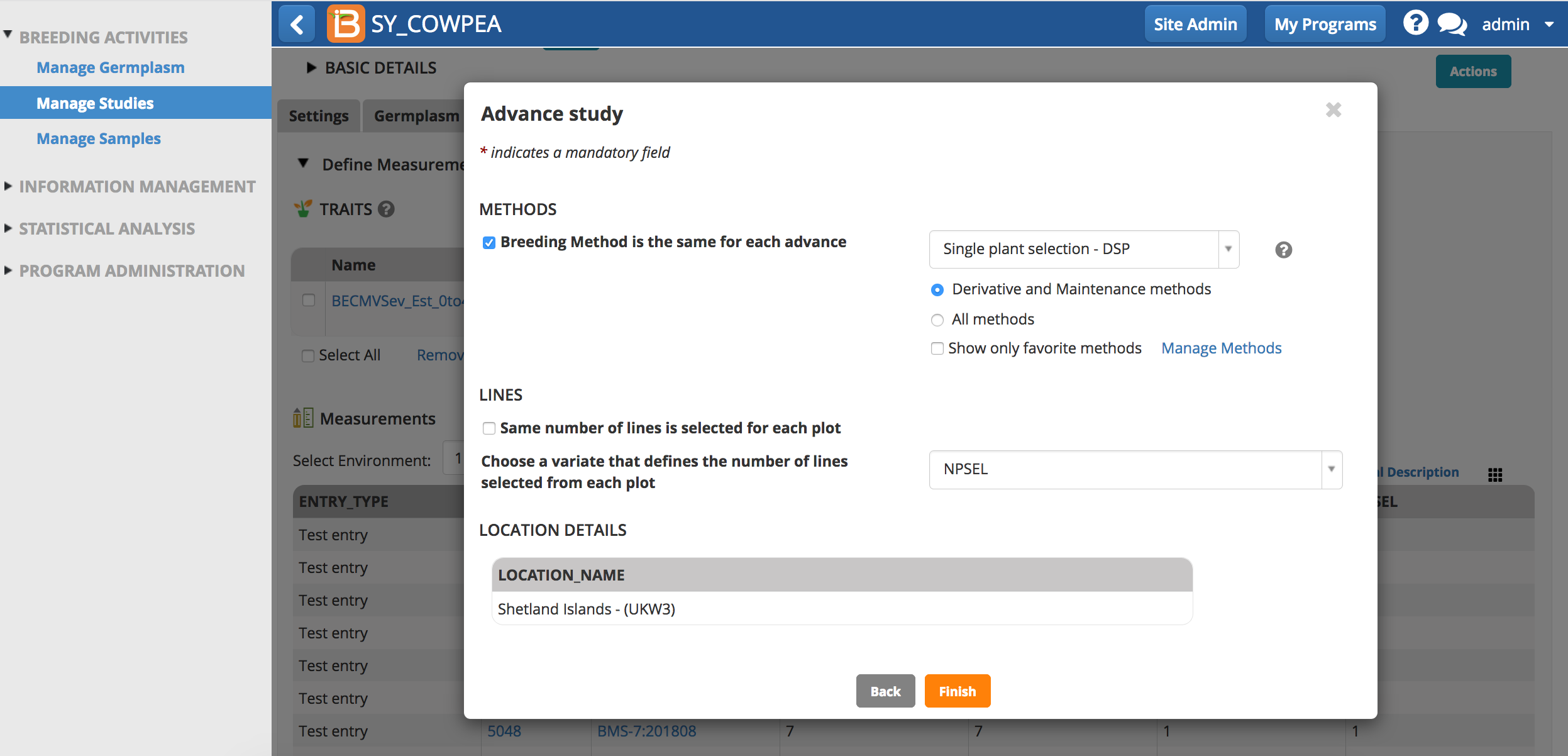
- Choose a breeding method. Derivative and maintenance breeding methods are filtered by default since these are the most common for advancements. Deselect 'All plots are selected'. Choose the selection variate that defines the number of lines advanced from eah plot. Finish.
- Review the advanced lines and select Finish.
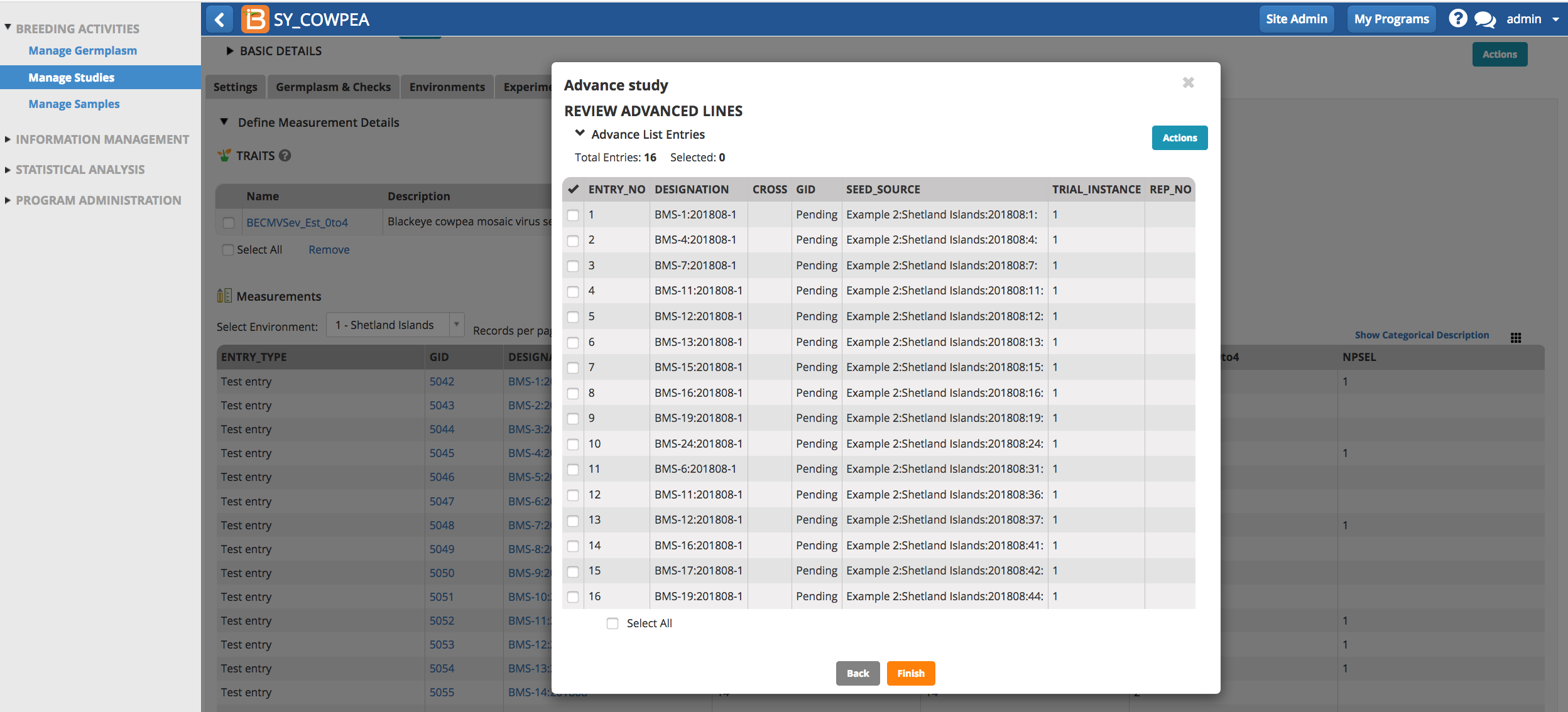
Notice that the pending lines have been automatically named. For example the designation, BMS-1-201808-1, is a concatenation of the parent line, BMS-1-201808, and the plant sequence number, 1). This is the default naming convention associated with the breeding method, single plant selection. See your system administrator if you would like to change the default naming conventions.
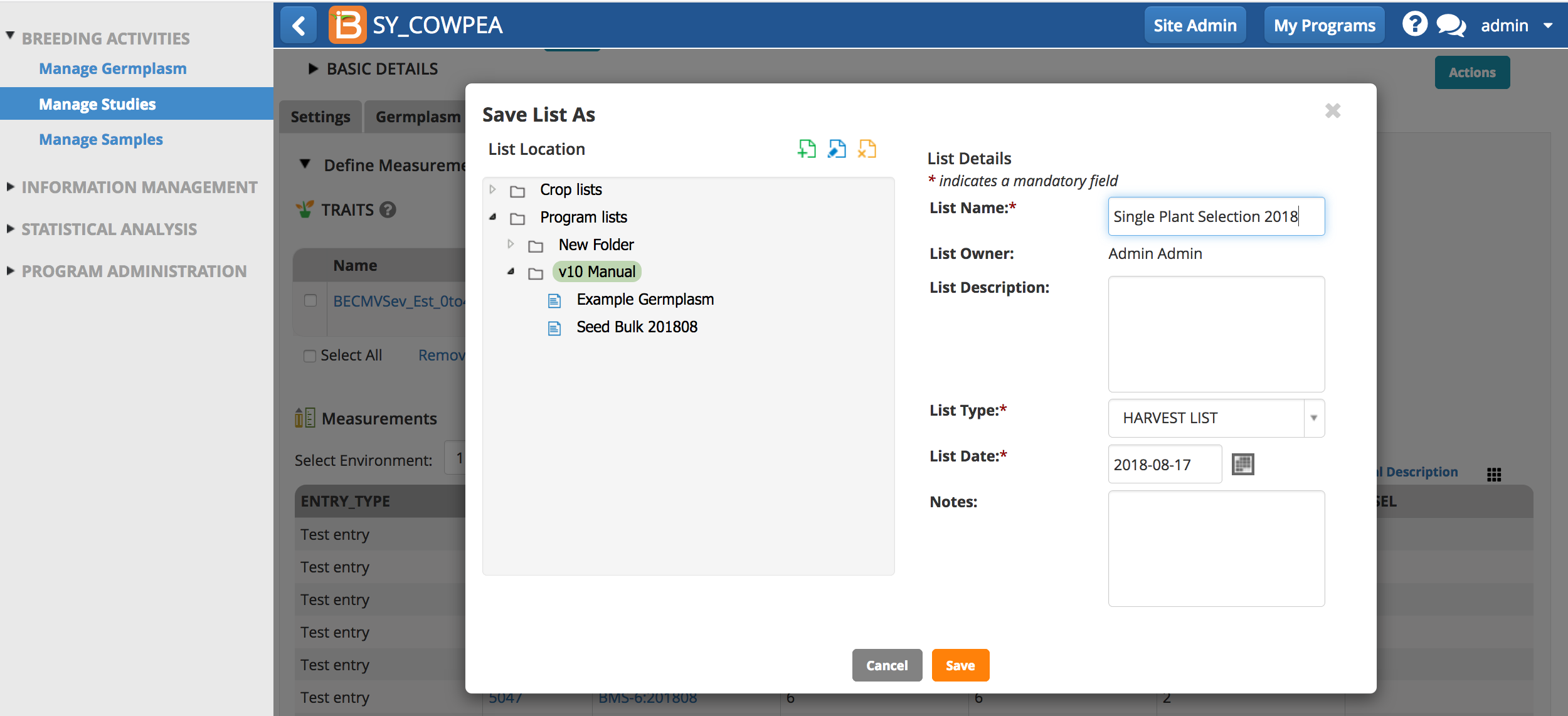
- Specify the folder where the list will be saved. Name the list and add optional information. Save.
With Plant ID
If you need a unique identifier (UID) for individual plant observations, create a plant sub-observation data set (see more Observations & Sub-Observations). The plant sub-observation UIDs are suitable for barcoding individual plants within a plot. Advance from the plant sub-observation dataset.
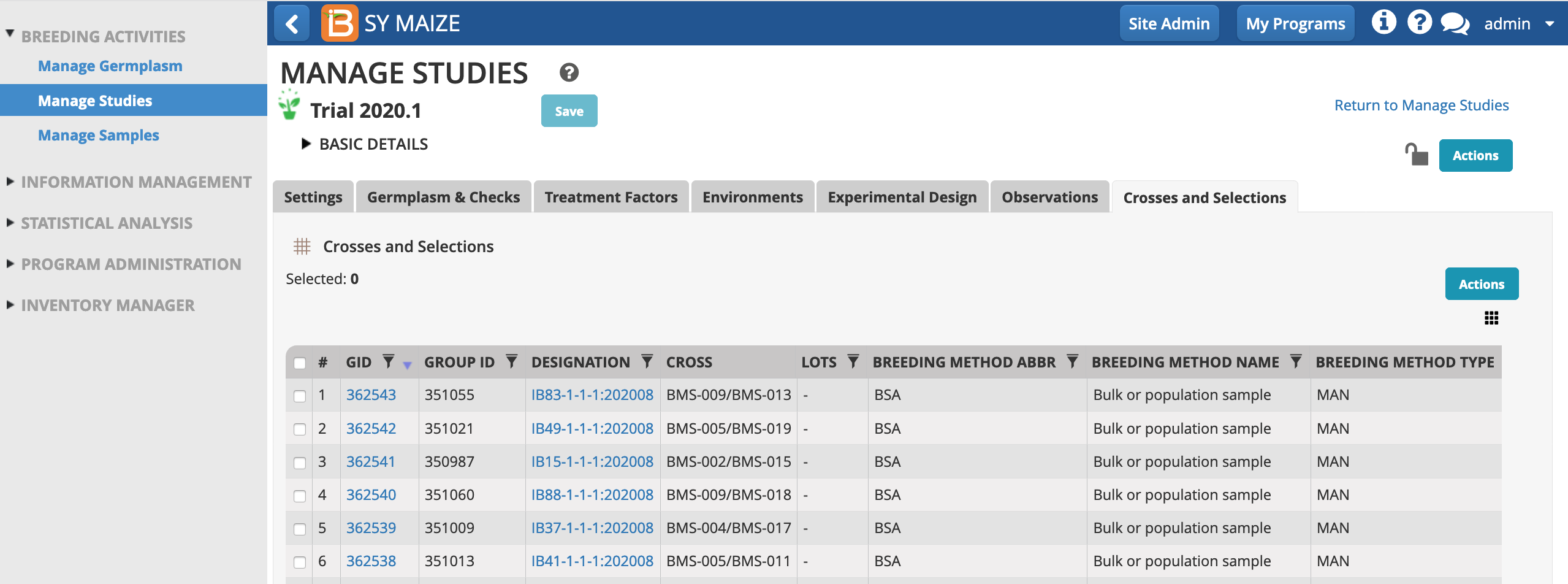
Crosses and Selections Tab
The advancing populates the Crosses and Selections tab. Additional crosses and selections from this nursery can be collated in this table. You are now able to harvest Crosses and Selections by first creating lots. See more in Manage Inventory.