One purpose of the doubled haploid (DH) study is to advance the DH lines by seed increase. After completion of the diallel cross, the remaining ears in the plot are bagged to insure selfing for inventory increase.
Create Advancement in Database
Advancement Note
Breeding methods are generally considered advancements when the method is expected to maintain or decrease genetic diversity . DH lines are ~100% homogygous and advancement of a DH line is expected to create genetically identical lines.
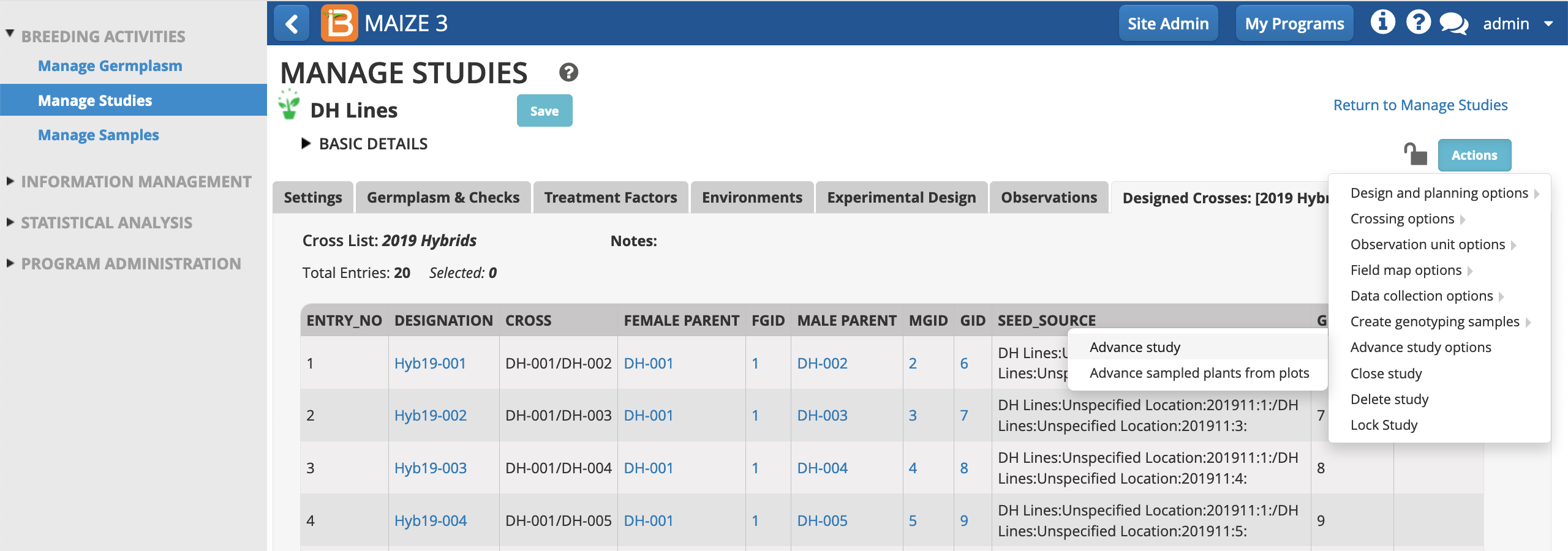
- Select Advance study from the DH Lines study Actions menu.
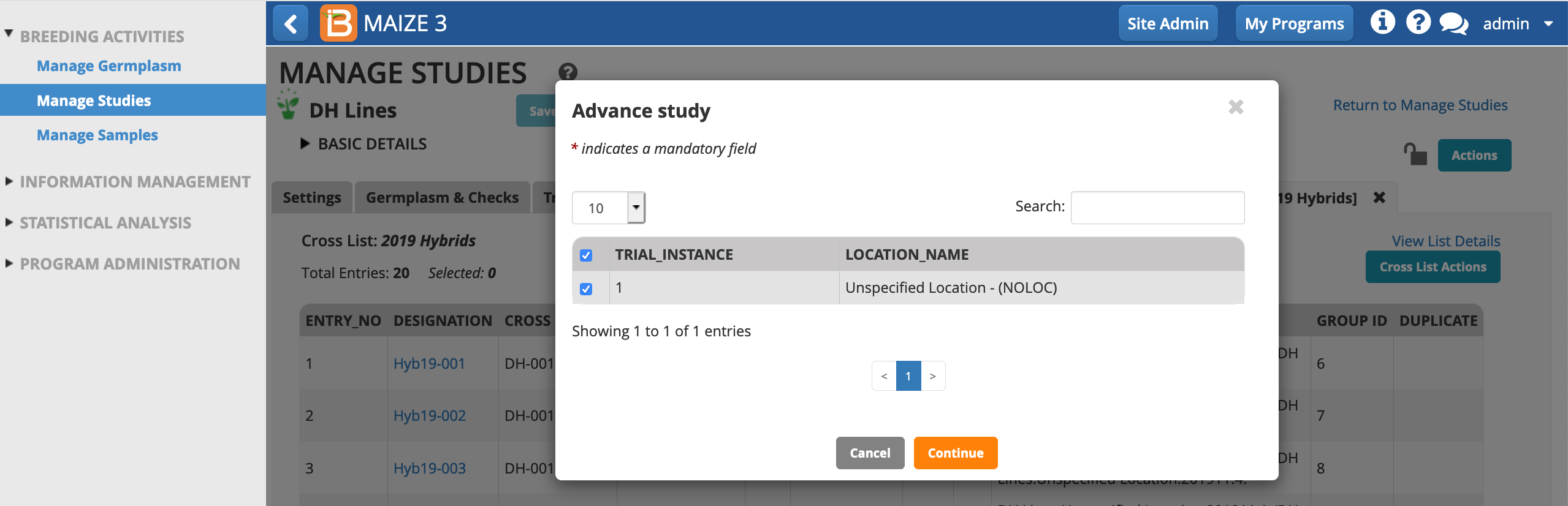
- Continue. (This study has a single location, which is selected by default.)
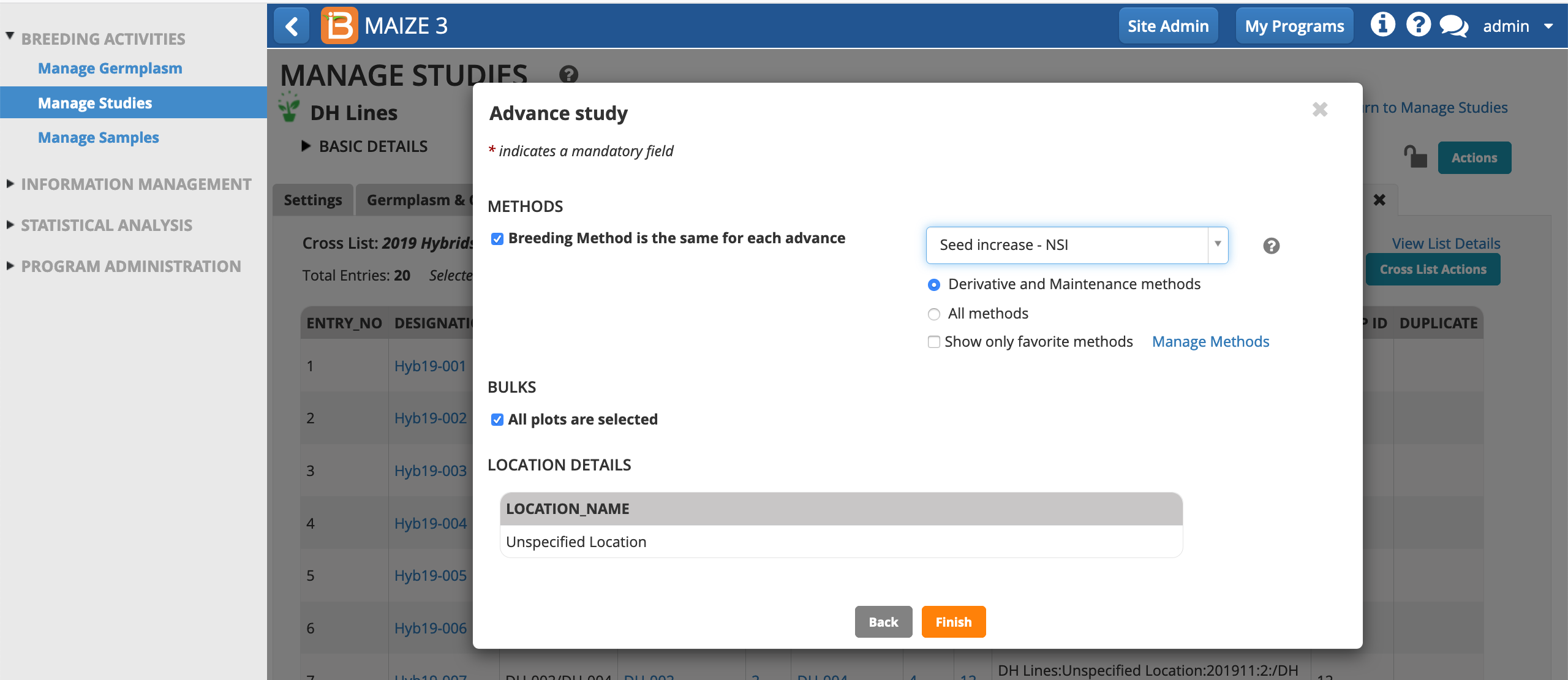
Breeding Method Note
The BMS comes preloaded with default breeding methods that determine offspring automatic naming conventions. Breeding methods are somewhat customizable, but most methods are supported by the defaults.
-
Choose the' Seed Increase - NSI' breeding method and allow all plots be selected. Finish.
- Review the pending advancement. Finish to create the advanced germplasm in the BMS.
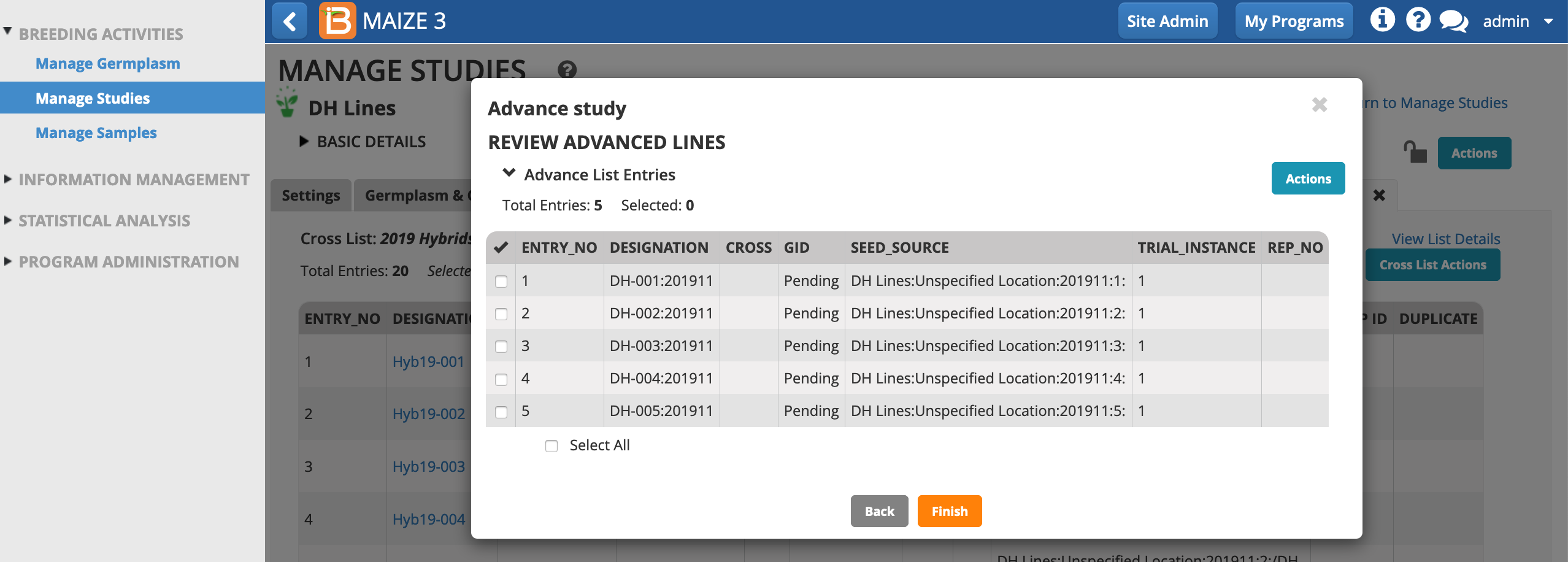
Notice the default automatic naming convention for seed increase, DH-001:201911. The DH line name is appended with year and month of the increase - providing a human readable description of the increase.
- Save the seed increase list.

Conclusion
After saving, the advance list is created in the BMS database. The germplasm list is available to create labels for selfing bags and seed harvesting. In later tutorials, you will have an opportunity to generate the stock list and record harvest details.
- Select the first advance, DH-001:201911, to reveal germplasm details.
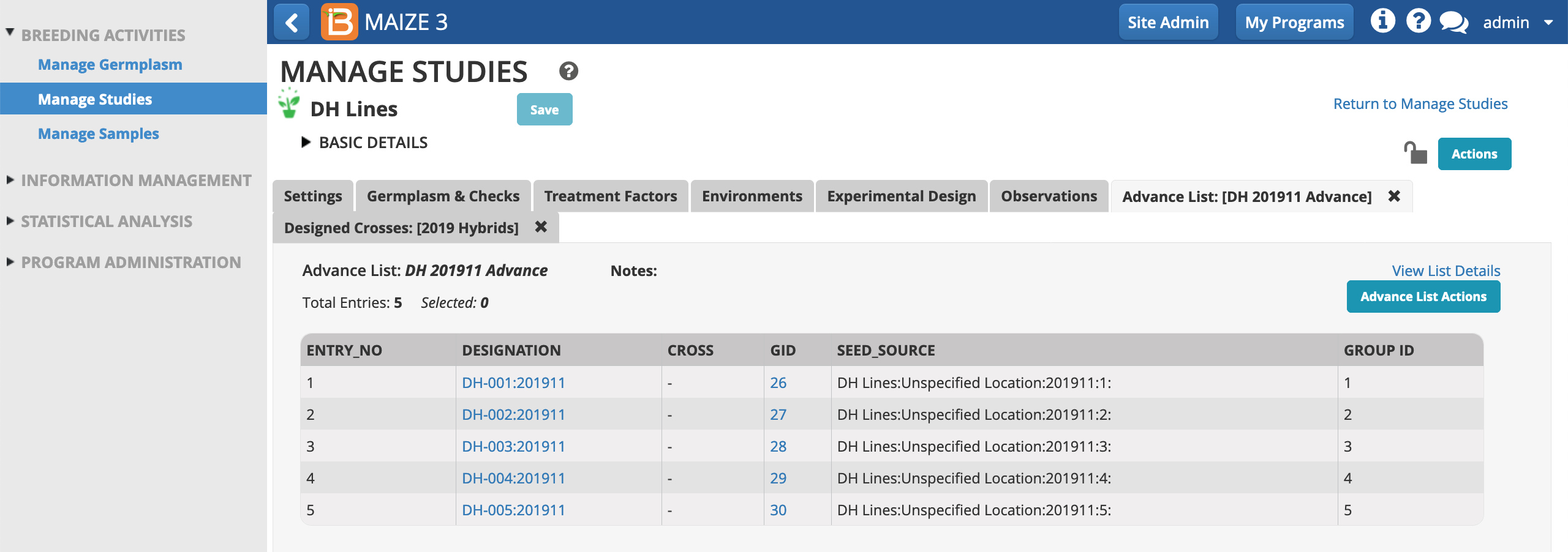
- View Pedigree Graph.
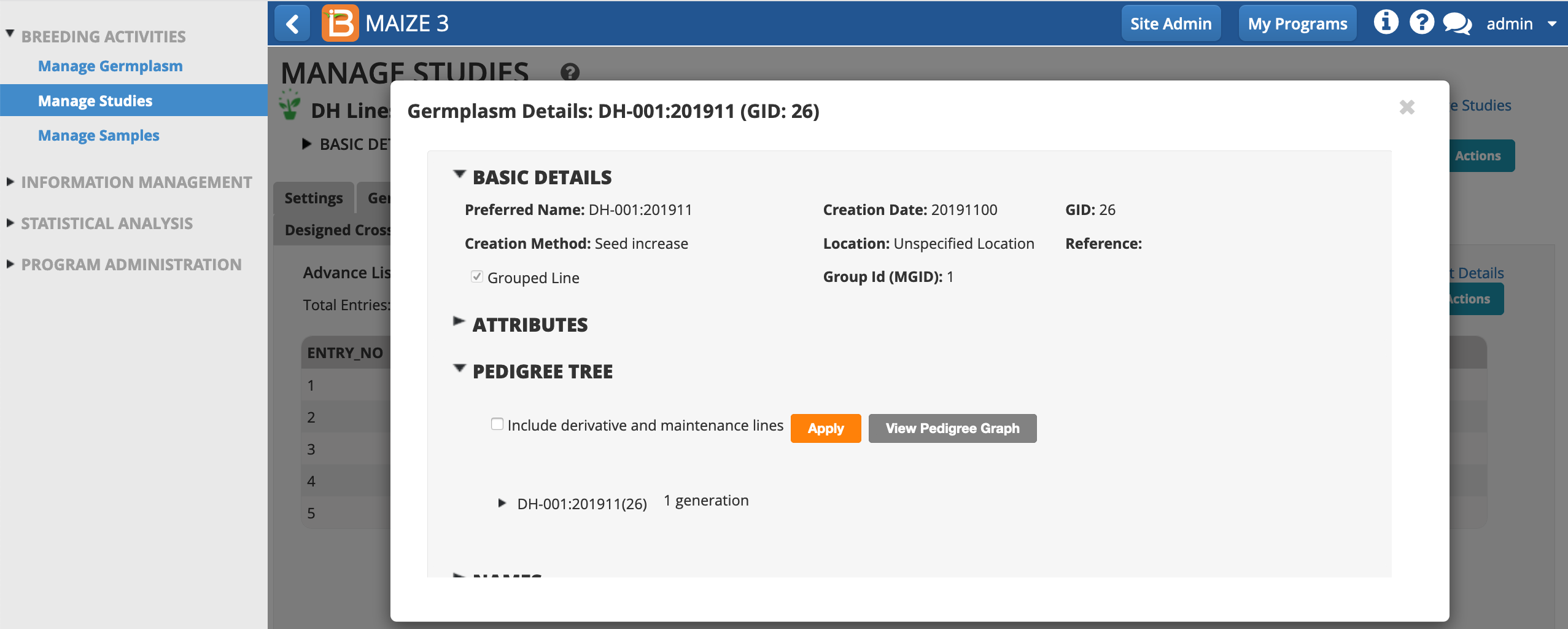
Notice that the first advance DH-001:201911 inherits the same GROUP ID as the progenitor, DH-001, line.
- Derivative and maintenance lines are excluded from the pedigree graph by default. Include derivative and maintenance lines. Display.
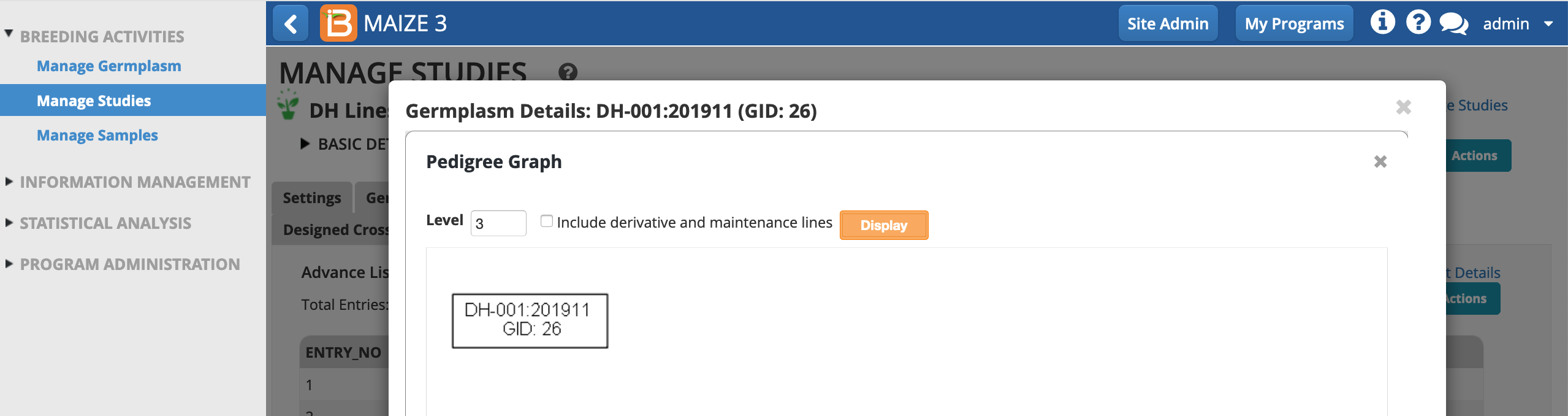
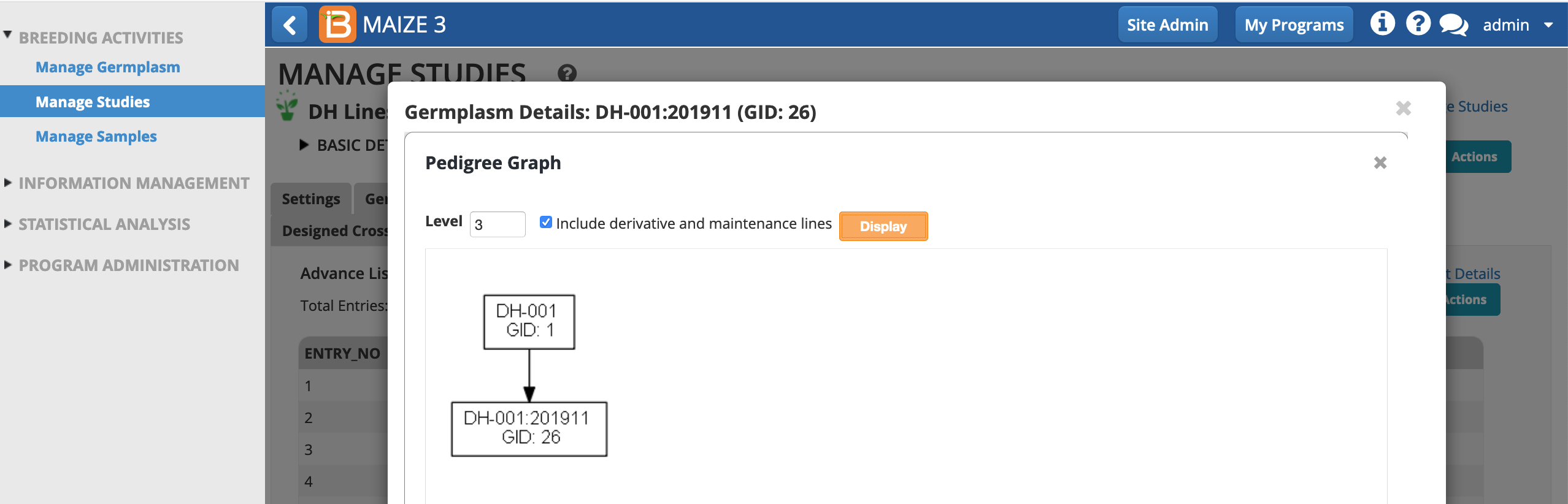
DH-001 and DH-001:201911 are distinguished by different breeding histories and GIDs. The genetic uniformity of DH-001 and DH-001:201911 is established by the shared GROUP ID.